
Unveiling the Follicle’s Hair Anatomy
Do you know what your hair is made of? Understanding the anatomy and structure of hair can help you take better care of your locks.
In this complete guide, we’ll explore the composition of hair, how it grows, and what can impact hair health. Read on to become an expert on all things related to hair anatomy!
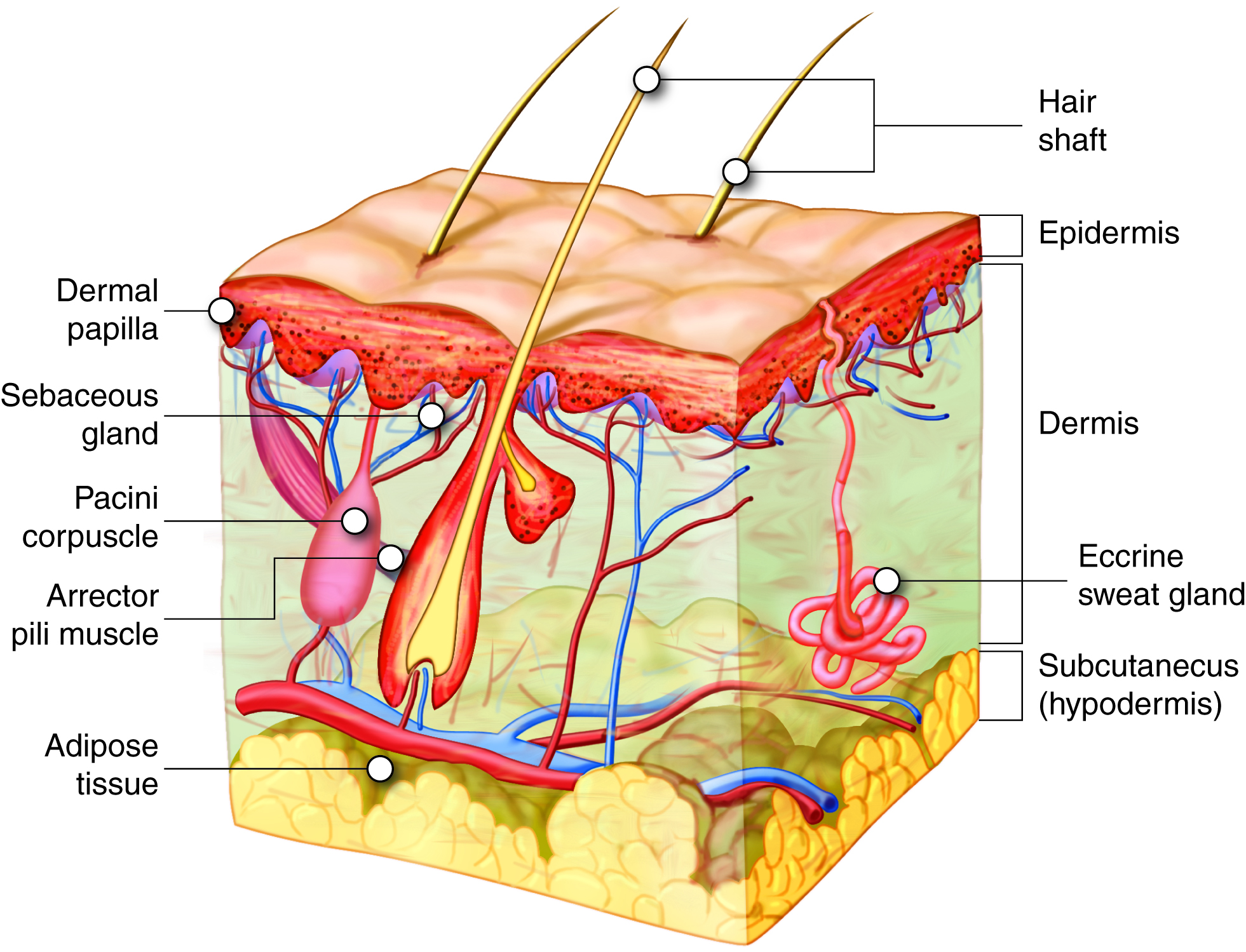
Hair Anatomy: What is Hair Made Of?
Hair is made of a protein called keratin that is produced in hair follicles in the outer layer of skin. The hair follicle is the small cavity in the skin from which hair originates and grows.
Keratin is the same protein that makes up nails and the outer layer of skin. There are three distinct layers that make up each strand of hair:
- Cuticle – The outermost layer made up of overlapping scales that protect the hair shaft. It controls shine and smoothness.
- Cortex – The middle layer full of keratin fibers that provide structure and strength. It contains melanin which gives hair its color.
- Medulla – The soft inner layer made of cells and air pockets. Not all hair contains this third layer.
In addition, hair contains small amounts of water, lipids, pigments like melanin, and minerals like zinc, copper and iron. The specific combination of these components give hair its unique qualities like texture, color and strength.
The 3 Stages of the Hair Growth Cycle
Hair grows in cycles and goes through three distinct phases:
1. Anagen (Growth Phase)
This is the active growth phase where hair rapidly divides and grows around half an inch per month. Scalp hair stays in this phase for 2-7 years.
2. Catagen (Transition Phase)
This short 2-3 week phase signals the end of active growth. The hair follicle shrinks and detaches from the blood supply.
3. Telogen (Resting Phase)
In this phase which lasts 2-3 months, the hair stops growing and eventually falls out. The hair follicle remains dormant for a few weeks/months before the cycle starts again.
As some hairs are growing, others are in the resting phase, which is why it’s normal to shed 50-100 hairs per day.
Different Types of Hair
There are a few different types and textures of hair that people can have:
- Straight – Straight hair has the most shine and the strands lay flat with no bend or curl pattern. It is one of the most common hair types.
- Wavy – Wavy hair has a loose S-shaped pattern and added volume. It is easy to style and lies somewhere between straight and curly.
- Curly – Curly hair with tight ringlets and coils has the most texture. It can be dryer and more fragile so needs extra moisture.
- Coiled – This is a tighter, extremely curly hair type common in African hair. The coils form tight zigzags or spirals.
- Kinky – This refers to very tightly coiled hair with a zig-zag pattern that grows in small corkscrews.
What Impacts Hair Health?
Many internal and external factors can affect the hair growth cycle and overall health of your hair. Here are some of the main influences:
Genetics – Your DNA plays a major role in characteristics like hair texture, thickness, growth patterns and potential for baldness.
Hormones – Hormonal changes from puberty, pregnancy and menopause can disrupt the natural hair cycle.
Medical conditions – Thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases and nutritional deficiencies can cause excessive shedding or hair loss.
Medications – Drugs like antidepressants, blood pressure meds and chemotherapy can lead to temporary or permanent hair loss.
Stress – High stress hormone (cortisol) levels can shift hairs from growth phase to shedding phase prematurely.
Hair care – Heat styling, tight hairstyles, harsh chemical products and overprocessing can damage the cuticle.
Diet – Getting enough protein, iron, zinc and vitamins (B, C, D) provides the nutrients hair needs to grow strong.
Aging – As we get older, hair cycles slow down and regrowth happens slower and finer. Baldness depends on genetics.
7 Tips for Healthy Hair
Caring for your hair properly is important for its overall health, strength and shine. Here are top tips:
- Use gentle, sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners
- Let hair air dry instead of using hot tools like blowdryers or straighteners
- Avoid tight hairstyles like ponytails or buns that pull on hair follicles
- Get regular trims to prevent split ends from travelling up the hair shaft
- Eat a balanced diet high in protein, iron, zinc and vitamins
- Take supplements like biotin, vitamin D or collagen if hair is thinning
- Reduce stress through yoga, meditation or other relaxation techniques
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 3 main structures of hair?
The cuticle protects the cortex and medulla. The cortex gives hair strength. The medulla is a soft core that not all hairs have.
What controls the hair growth cycle?
The hair growth cycle is controlled by hormones, genetics, age, and factors like stress, nutrition and medications. Hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone play a key role in regulating the phases of hair growth.
What is a hair follicle?
A hair follicle is the cavity or sac within the skin from which a hair originates and grows. The hair follicle contains connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, the root of the hair, and sebaceous (oil) glands.
How does hair grow out of the follicle?
Hair grows from the root in the follicle. The cells at the base divide rapidly to form the hair shaft that emerges on the surface. The follicle anchors and nourishes the root as it grows. Sebum lubricates the emerging hair.
What causes hair to turn grey?
As we age, our hair follicles produce less melanin – the pigment that gives hair its color. With less melanin, new hair strands grow in lighter and turn grey. Factors like genetics, stress, and smoking can also cause premature greying.
What are the symptoms of hair follicle disorders?
Symptoms of conditions like alopecia areata, folliculitis, and lichen planopilaris include excessive shedding, bald patches, scaling, pimples on the scalp, and red, itchy inflamed follicles.
How many hairs does the average person have?
The average person has around 100,000 to 150,000 hairs on their head. We have a range of different hair types including vellus hair, terminal hair, lanugo hair, etc. The total number of hairs varies by age, sex, and body part.
Do hair follicles heal after injury?
If the follicle root remains intact, hair can regrow after an injury. But if the follicle stem cells are destroyed, scar tissue forms and prevents regeneration. Proper wound care and treatment help optimize healing and hair regrowth.
What impacts hair health and growth?
Genetics, hormones, age, nutrition, stress levels, medications, hair care practices, and medical conditions like thyroid disorders affect hair health and growth cycles. A balanced diet, scalp massage, avoiding harsh products, and managing stress support healthy hair.